|
| <- prev |
| About Erase Method-> About Secure Erase/Sanitize |
What is "Secure Erase", "Sanitize"?
"GreenPepper PRO"-"Boot up Erase Program", and "Windows
Erase Program"(only when runnin on WindowsPE) have "Secure Erase" and "Sanitize"
functions.
"Secure erase" is superior to normal erasure in terms of
security and processing speed, but its execution environment is limited and
there are uncertainties due to processing outside the control of the software.
Please use it after fully understanding the features.
"Sanitize" is a
newer standard than "Secure erase", and if it is a compatible hard disk or SSD,
there are less restrictions on the execution environment (Some PCs have some
restrictions) and it can be executed
more easily. In addition, since it is possible to grasp the progress status
during execution, it is possible to erase more reliably. However, currently
fewer disks support "Sanitize" than "Secure erase".
Supported disks by "GreenPepper PRO"(Boot up Erase
Program) ver. 4.6.4 or later
・ ATA(IDE,SATA)
disk (include SSD) ・ ・ ・ SecureErase/Sanitize
・ NVMe drive ・ ・ ・ SecureErase/Sanitize
・ eMMC drive ・ ・ ・ SecureErase/Sanitize
・ Other(SAS, RAID etc.) ・ ・ ・ only
normal erase
Supported disks by "GreenPepper PRO"(Windows
Erase Program on WindowsPE) ver. 4.7.1 or later
・ ATA(IDE,SATA)
disk (include SSD) ・ ・ ・ SecureErase/Sanitize
・ NVMe drive ・ ・ ・ SecureErase/Sanitize
・ eMMC drive ・ ・ ・ only normal erase
・ Other(SAS, RAID etc.) ・ ・ ・ only
normal erase
Normal erasing process
The normal erasing process that "GreenPepper PRO" also has is realized by
performing the process of writing data by specifying the location and value for
the entire disk area.
Secure Erase/Sanitize process
Secure erase and sanitize processing are functions provided by ATA (PATA ,
SATA), NVMe, and eMMC disk itself. By sending a command to perform Secure erase
/ Sanitize to the corresponding disk, the erase process is executed inside the
disk.
When Secure erase / Sanitize is recommended
1.When there are many "Reallocated sectors"
Hard disks are processed in units called sectors (usually 512 or 4096bytes). If
an error occurs frequently in a certain place due to a defect on the disk
surface, the disk isolates the bad sector by allocating the area that it has as
a spare as a substitute for the bad sector.
There may be some data left in the reallocated bad sectors, but the detached bad sectors
cannot be erased by normal erasing because they are completely inaccessible to
the software.
There are two types of secure erase. Normal "Secure Erase"
does not erase reallocated bad sectors, but "Enhanced Secure Erase" erases
reallocated bad sectors as
well. The "Sanitize" process also erases reallocated bad sectors.
The following points should be considered regarding the necessity of erasing
reallocated sectors.
・ Cannot be read by normal software processing
・
Because it is "bad", the possibility of reading is low.
・ Even if secure
erasure is performed, it is uncertain whether it can be completely erased
because it is defective.
You can check the number of "reallocated sectors" on the "GreenPepper PRO"
screen. 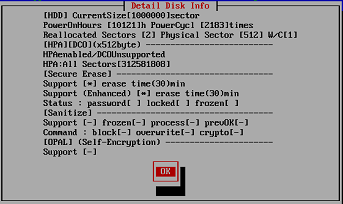
* Detailed disk information display screen in "Boot up Erase Program"
2.
flash drive media such as SSD (ATA), NVMe, eMMC
Since flash drive has a finite limit on the number of rewrites, SSDs and the
like often have a built-in mechanism that averages the writing
locations (Wear Leveling) so that writing does not concentrate on the same location.
With
these mechanisms, the correspondence between the write position (sector)
specified by the software and the memory cell where the write is actually
performed is dynamically changed. In addition, the memory for allocation is
often more than the total capacity available to the user. Therefore, even if
the entire disk is written (erased), the entire installed memory may not
always be erased.
In addition, in order to avoid time-consuming erasing processing during normal
writing, the target memory area may not be erased and area replacement may be
performed (dynamic memory mapping).
For SSD (ATA), eMMC, etc. that support
secure erase / sanitize, it is possible to avoid "Wear Leveling" and dynamic
memory mapping by performing secure erase / sanitize processing , and erase
all installed memory cells.
3. When processing speed is required
Since the secure erase / sanitize process is performed inside the disk, it is
executed at the highest processing speed of the disk hardware. Therefore, it
can be processed faster than normal erasing.
Especially for flash drive
(SSD, NVMe, eMMC), secure erase / sanitize processing is considerably faster.
However, if it is a hard disk, the normal erasing process in "Green Pepper
PRO" is performed at a very high speed, so it is possible to perform the
processing in a time close to secure erasing.
See
"Time required to erase disk"
Problems with Secure Erase/Sanitize
Secure Erase / Sanitize has many advantages as mentioned above, but it also
has the following problems.
・ The processing environment is limited. (See "Details of Secure Erase /
Sanitize" below)
・ Especially for Sanitize, there are not many HDDs and
SSDs that support it.
・ Since it is a process outside the control of the
software, the status cannot be grasped, the content of the process depends on
the manufacturer's implementation and cannot be known, and even if a write
error occurs, it may not be known.
Therefore, in "Green Pepper PRO", after
Secure Erase and Sanitize, we provide normal writing/reading process to check
the contents of the disk.
Details of Secure Erase/Sanitize
ATA (SATA) Secure Erase processing details
There are two types of secure erase: normal "Secure Erase" and "Enhanced
Secure Erase". "Enhanced" is a newer and more reliable erasing method. If the
disk supports "enhanced", "Green Pepper PRO" will automatically select
"enhanced".
・ Secure Erase
Erase the entire disk with zero. "Reallocated sectors" that have been detached
are not erased.
・ Enhanced Secure Erase
Erase the entire disk with zero or a value specified by the manufacturer.
"Reallocated sectors" that have been detached are also erased. * The same value
may not be written to the entire disk, such as when a random value is written.
Therefore, a verification error may occur in the read verification process
performed just after secure erase.
The time required for Secure Erase is written in advance on the disk by the
manufacturer. "Green Pepper PRO" reads the value and display it on the screen.
ATA(SATA) Sanitize processing details
The sanitize process erases all user areas, including reallocated bad
sectors and unallocated areas.
There are three types of ATA standard
sanitize process as follows.
・ CRYPTO SCRAMBLE: Delete the encryption key
on the encryption-compatible HDD / SSD.
・ BLOCK ERASE: Performs memory block
erasure processing, especially on SSDs.
・ OVER WRITE: Erase by overwriting.
In "Pepper PRO", the following processing is performed.
O: supported X:
unsupported -: any
| CRYPT | BLOCK ERASE |
OVER WRITE | Content of processing |
| O | O | - | CRYPT SCRAMBLE + BLOCK ERASE |
| O | X | O | CRYPT SCRAMBLE + OVER WRITE |
| O | X | X | CRYPT SCRAMBLE |
| X | O | - | BLOCK ERASE |
| X | X | O | OVER WRITE |
NVMe Secure Erase/Sanitize processing details
NVMe drives have more memory than the user's available capacity and are configured with constantly changing memory allocations (dynamic memory mapping). NVMe Secure Erase erases the entire device, including unallocated space. Note that if the device is divided into multiple drives (NameSpace), the entire device will be erased, including unselected drives, depending on the model.
The processing content is almost the same as the ATA drive.
eMMC Secure Erase/Sanitize details
eMMC drives have more memory than the user's available capacity and are configured with constantly changing memory allocations (dynamic memory mapping). In the Sanitize process of eMMC flash drive, the entire user's available capacity is erased (Erase) and then the non-allocated area is erased (sanitized). Secure Erase performs memory erase processing only on the user's available capacity.
In "Green Pepper PRO", Sanitize processing is performed when sanitize is supported, and Secure Erase is performed when sanitize is not supported (secure erase is supported).
Settings for secure erase / sanitize processing method on ATA / MVMe / eMMC drives
The processing method in "Secure Erase / Sanitize" can be changed arbitrarily.
See "Utilities"-> "Set Secure Erase Method / Unfreeze".
Disk / Interface support
To perform Secure Erase, the disk itself must comply with the Secure Erase standard. If it is an ATA (PATA, especially SATA) disk that has been on the market in recent years, it seems that the disk is compatible in many cases.
However, it is often the case that disks less than 100G several years ago do not support enhanced processing. There are many disks that do not support Sanitize.
In addition to being supported by the disk, the disk interface you are using (both hardware and software) must pass the ATA command processing for Secure erase. For example, SATA and PATA connected to Intel chipset (ICH7,8,9,10, etc.) can be processed in many cases. But disks connected by USB interfaces may not be processed even if it is the same disk drive.
Whether processing is possible or not
Even if the disk and interface are compatible, processing may not be possible depending on the disk status.
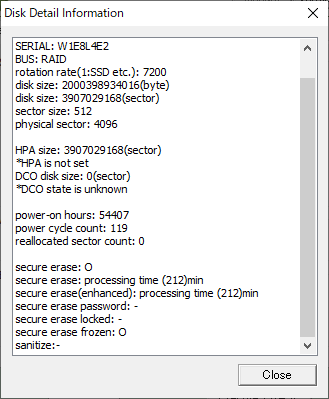
* Detailed disk information display screen in "Windows Erase Program"
Secure Erase "Frozen" state/ATA drive
If a freeze command is sent to the disk and the disk is in a frozen state, secure erase-related operations cannot be performed.
The freeze command is automatically sent from your computer to the disk when you turn on the power.
Normal disk read / write works fine even if the disk is frozen state.
On many PCs, the BIOS sends a freeze command to all disks at boot time.
It is to prevent malicious software such as viruses from setting passwords or erasing the disk. In such a PC, the disk is originally unfrozen when the power is turned on, but immediately after that, BIOS sends a freeze command unconditionally, so if you look at the state of the disk after the PC starts up, It will be frozen.
*Freezing processing for Sanitize(ATA) is not performed on many PCs, but it is frozen on some PCs.
In order to release the frozen state, it is necessary to either prevent the Freeze command from being sent by changing the BIOS settings, or to connect the disk to a PC that does not send such a command. It cannot be canceled by software processing.
It is possible to turn the power of the disk off and on while the PC is running, but there is a risk of damaging the disk and other parts, so please be aware of the danger and do so at your own risk.
* In general, it seems that the SATA power supply is relatively safe even if it is inserted or removed when PC is running. IDE power cable should not remove or insert.
Unfreeze process (ver 4.7.1 or later)
In order to unfreeze the ATA drive, we have implemented a process that suspends the PC and then resumes it. (Only when booting from a CD/USB memory with the "Boot up erase program").
There are two ways to do this: specify the option at startup, or select "Utility"/"Set Secure Erase Method/Unfreeze".
However, in order to perform this process, the video chip of the PC must be compatible. If it is not compatible, it will not be executed even if the process is selected, or the screen will remain black after processing and nothing will be displayed.
* NVMe drives do not have a frozen state due to their specifications, but with some drives, secure erasing will result in an error under normal conditions, and processing may be possible by "unfreezing" processing.
See "Boot from CD/USB flash drive".
See "Utilities"-> "Set Secure Erase Method / Unfreeze".
See "Supported display chips"
Secure Eras "Password Locked" state/ATA drive
One of the standards for secure erasure is the setting of a hard disk password. When the power of the password-set disk is turned on, the disk becomes "locked state" and you cannot access the disk including reading and writing.
To unlock the "locked state", you need to unlock with the set password or delete the password.
Of course, if you don't know your password, you can't unlock / delete it.
・ "Frozen" state
Read / write is possible. Password setting/deleting and unlocking are not possible. Secure erase is NOT possible.
Cannot be canceled by command.
・ "Password Locked"state
Read / write is NOT possible. Secure erase is NOT possible.
The status can be released by the unlock / password delete command. Password required.
Secure Erase / Sanitize processing procedure
"Green Pepper PRO" automatically performs a series of processes internally, so you do not need to be aware of it. However, if you know the process it will be easier for recovery when Secure erase / Sanitize is interrupted.
To perform secure erase on an ATA disk, you must set a hard disk password in advance and specify it during the secure erase process. In "GreenPepper PRO", the word "pass" is set as the disk password (master) and processing is performed.
Problems when Secure Erase is interrupted
If the Secure erase process is interrupted in the middle, the disk erase is not completed.
Please execute the erasing process again.
Problems when ATA disk Sanitize is interrupted
Depending on the supported specifications, the Sanitize process will continue the next time the power is turned on.
In that case, normal reading and writing will NOT be possible.
It must be left power-on until the Sanitize process is complete.